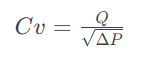Valve Flow Coefficient (Cv) Explained: Understanding the Basics
The Valve Flow Coefficient (Cv) is a critical parameter in fluid dynamics and is widely used in the design and selection of valves for various industrial applications. It represents the flow capacity of a valve and plays a key role in determining the efficiency and performance of fluid control systems. Let’s delve into the basics of Cv and its significance.
What is Valve Flow Coefficient (Cv)?
The Cv value is a numerical representation of the flow rate of a valve under specific conditions. It is defined as the flow of water at 60°F (15.6°C) in gallons per minute (GPM) that will pass through a valve with a pressure drop of 1 psi. Essentially, it quantifies the valve’s ability to control the flow of a fluid.
Formula for Calculating Cv:
The Cv value can be calculated using the following formula:
: Valve Flow Coefficient
- : Flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM)
- : Pressure drop across the valve in pounds per square inch (psi)
Importance of Valve Flow Coefficient:
Selection of Valves:
- Cv is crucial in selecting the appropriate valve for a specific application. It helps engineers and designers choose valves that can handle the required flow rates efficiently.
System Efficiency:
- Understanding Cv ensures that the fluid control system operates at optimal efficiency. Properly sized valves contribute to better system performance.
Flow Control Accuracy:
- Valves with higher Cv values provide better control over fluid flow. This is particularly important in processes where precise flow control is essential.
Comparing Valve Performance:
- Cv allows for easy comparison between different valves. Engineers can evaluate and choose valves based on their Cv values for specific operating conditions.
Factors Affecting Cv:
Valve Design:
- The internal geometry and design of the valve significantly impact its Cv value. Different valve types (e.g., globe, ball, butterfly) have distinct effects on flow characteristics.
Fluid Properties:
- The type of fluid being controlled (viscosity, density) influences Cv. Valve sizing may vary for gases, liquids, or multiphase fluids.
Temperature and Pressure:
- Cv is temperature and pressure-dependent. Changes in these parameters affect the fluid’s density and viscosity, impacting the valve’s performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the Valve Flow Coefficient (Cv) is essential for effective fluid flow control. Proper selection and sizing of valves based on Cv values contribute to efficient system operation, accuracy in flow control, and overall performance in various industrial applications.
 Ontrose industrial corporation Inc. Engineering and supply of industrial projects
Ontrose industrial corporation Inc. Engineering and supply of industrial projects